Indications/Uses
Treatment of bronchial asthma, pulmonary disease with spastic bronchial component and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Dosage/Direction for Use
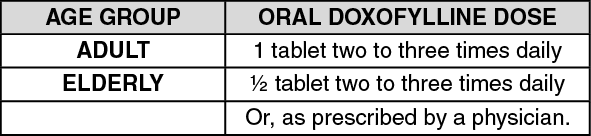
Overdosage
If a potential overdose is established, the patient may present with severe arrhythmias and seizure. These symptoms could be the first sign of intoxication. Treatment of doxofylline overdosage is symptomatic and supportive. It includes withdrawal of the drug.
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to doxofylline or other ingredients in the product; Patients with acute myocardial infarction, hypotension and in breastfeeding women.
Special Precautions
Xanthine half-life may be increased and clearance decreased in patients with liver disease, congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive lung disease or concomitant infections. In these cases, the dose of doxofylline may be reduced.
Use with caution in patients with following conditions: Elderly; Hyperthyroidism; Hypoxemia; Peptic ulcer; Renal or hepatic disease; Cardiovascular disorders including cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, acute myocardial injury, hypertension, or congestive heart failure.
Use in Elderly: Doxofylline should be administered cautiously to elderly patients. Dosage may be reduced and careful monitoring of doxofylline plasma concentrations may be required to avoid severe toxicity.
Use in Children: Doxofylline should be administered cautiously to young children.
Use with caution in patients with following conditions: Elderly; Hyperthyroidism; Hypoxemia; Peptic ulcer; Renal or hepatic disease; Cardiovascular disorders including cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, acute myocardial injury, hypertension, or congestive heart failure.
Use in Elderly: Doxofylline should be administered cautiously to elderly patients. Dosage may be reduced and careful monitoring of doxofylline plasma concentrations may be required to avoid severe toxicity.
Use in Children: Doxofylline should be administered cautiously to young children.
Use In Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy: The safe use of doxofylline during pregnancy has not been established. Doxofylline should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Lactation: Methylxanthines are distributed into all body compartments. They cross the placenta and are distributed into breast milk. Doxofylline is contraindicated in breastfeeding mothers.
Lactation: Methylxanthines are distributed into all body compartments. They cross the placenta and are distributed into breast milk. Doxofylline is contraindicated in breastfeeding mothers.
Adverse Reactions
After xanthine administration, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, headache, irritability, insomnia, tachycardia, extrasystole, tachypnea, and occasionally hyperglycemia and albuminuria, may occur.
Drug Interactions
Doxofylline should not be administered concomitantly with other methylxanthines, including beverages and foods containing caffeine.
Xanthine half-life may be increased and clearance decreased by interaction with cimetidine, allopurinol, propranolol, erythromycin, troleandomycin, lincomycin, ciprofloxacin, and anti-flu vaccine. In these cases, the dose of doxofylline may be reduced.
Xanthine half-life may be decreased and clearance increased by phenytoin, anticonvulsants, and smoking. In these cases, a higher dose of doxofylline may be required.
Synergistic toxicity with ephedrine and other sympathomimetics have been reported for xanthines.
Xanthines may potentiate hypokalemia caused by hypoxia or associated with the use of beta2-adrenoceptor stimulants (beta2-agonists), corticosteroids, and diuretics.
Xanthine half-life may be increased and clearance decreased by interaction with cimetidine, allopurinol, propranolol, erythromycin, troleandomycin, lincomycin, ciprofloxacin, and anti-flu vaccine. In these cases, the dose of doxofylline may be reduced.
Xanthine half-life may be decreased and clearance increased by phenytoin, anticonvulsants, and smoking. In these cases, a higher dose of doxofylline may be required.
Synergistic toxicity with ephedrine and other sympathomimetics have been reported for xanthines.
Xanthines may potentiate hypokalemia caused by hypoxia or associated with the use of beta2-adrenoceptor stimulants (beta2-agonists), corticosteroids, and diuretics.
Storage
Store at temperatures not exceeding 30°C.
Action
Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: Doxofylline, a bronchodilator, differs from theophylline by the presence of a dioxolane group in position 7. Doxofylline inhibits phosphodiesterase enzymes followed by an increase in cyclic-3',5'-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). cAMP mediates cellular responses such as bronchial smooth muscle relaxation resulting in bronchodilation.
The decreased affinity of doxofylline for adenosine A1and A2 receptors has been suggested to account for its better safety profile compared with theophylline. Studies on doxofylline have shown less pronounced clinically important arrhythmogenic and cardiostimulant effects.
Pharmacokinetics: Doxofylline is rapidly absorbed following an oral dose of 400 mg, with peak serum concentration being reached after 1 hour and steady state in 4 days. Absolute bioavailability is about 62.6%. Plasma protein binding is about 48%. Doxofylline is almost completely metabolized in the liver, with only one detectable metabolite (hydroxymethyltheophylline). Less than 4% of an orally administered dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. The mean elimination half-life is 7.01 ± 0.8 hours.
The decreased affinity of doxofylline for adenosine A1and A2 receptors has been suggested to account for its better safety profile compared with theophylline. Studies on doxofylline have shown less pronounced clinically important arrhythmogenic and cardiostimulant effects.
Pharmacokinetics: Doxofylline is rapidly absorbed following an oral dose of 400 mg, with peak serum concentration being reached after 1 hour and steady state in 4 days. Absolute bioavailability is about 62.6%. Plasma protein binding is about 48%. Doxofylline is almost completely metabolized in the liver, with only one detectable metabolite (hydroxymethyltheophylline). Less than 4% of an orally administered dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. The mean elimination half-life is 7.01 ± 0.8 hours.
MedsGo Class
Antiasthmatic & COPD Preparations
Features
Dosage
400mg
Ingredients
- Doxofylline
Packaging
Tablet 50's
Generic Name
Doxofylline
Registration Number
DR-XY43496
Classification
Prescription Drug (RX)
Product Questions
Questions

