Indications/Uses
Tablet: Treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible strains by the designated microorganisms: Pharyngitis/tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes; acute bacterial otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae (including β-lactamase-producing strains), Moraxella catarrhalis (including β-lactamase-producing strains) or S. pyogenes; acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis caused by S. pneumoniae, or H. influenzae (non-β-lactamase-producing strains only); acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis and secondary bacterial infections of acute bronchitis caused by S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae (β-lactamase negative strains), or H. parainfluenzae (β-lactamase negative strains); uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (including β-lactamase-producing strains) or S. pyogenes; uncomplicated urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli or Klebsiella pneumoniae; uncomplicated gonorrhea, urethral and endocervical, caused by penicillinase-producing and non-penicillinase-producing strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and uncomplicated gonorrhea, rectal, in females, caused by non-penicillinase-producing strains of N. gonorrhoeae, and early Lyme disease (erythema migrans) caused by Borrelia burgdorferi.
Injection: Alternative drug for infections due to susceptible organisms eg, otitis media, orbital cellulitis, urinary tract, skin and soft tissue, bone and joint infections and post-sphenectomy sepsis of unclear etiology.
Injection: Alternative drug for infections due to susceptible organisms eg, otitis media, orbital cellulitis, urinary tract, skin and soft tissue, bone and joint infections and post-sphenectomy sepsis of unclear etiology.
Dosage/Direction for Use
Tablet: Cefuroxime axetil may be administered with or after food at the following regimen, or as prescribed by the physician: Adults and Adolescents ≥13 years: Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis, Acute Bacterial Maxillary Sinusitis: 250 mg twice daily for 10 days.
Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis: 250 or 500 mg twice daily for 10* days.
Secondary Bacterial Infection of Acute Bronchitis: 250 or 500 mg twice daily for 5-10* days.
*The safety and effectiveness when administered for <10 days in acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis have not been established.
Uncomplicated Urinary Tract, Skin and Skin-Structure Infections: 250 mg twice daily for 7-10 days.
Uncomplicated Gonorrhea: 1000 mg once with single dose probenecid 1000 mg.
Early Lyme Disease: 500 mg twice daily for 20 days.
Children (Who can Swallow Tablet Whole): Acute Otitis Media and Bacterial Maxillary Sinusitis: 250 mg twice daily for 10 days.
Injection: Adults: Usual Dosage Range: 750 mg to 1.5 g every 8 hrs, usually for 5-10 days.
Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections, Skin-Structure Infections, Disseminated Gonococcal Infections and Uncomplicated Pneumonia: Recommended Dose: 750 mg every 8 hrs.
Severe and Complicated Infections, Bone and Joint Infections: Recommended Dose: 1.5 g every 8 hrs.
Bacterial Meningitis: Recommended Dose: 1.5 g every 6 hrs and should not exceed 3 g every 8 hrs.
Uncomplicated Gonococcal Infection: Recommended Dose: 1.5 g given IM as a single dose together with 1 g of oral probenecid.
Children: Normal Dose: 50-100 mg/kg/day, and may be increased to 150 mg/kg/day in cases of bone and joint infections, and 200-240 mg/kg/day for bacterial meningitis in equally divided doses, every 6-8 hrs.
Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis: 250 or 500 mg twice daily for 10* days.
Secondary Bacterial Infection of Acute Bronchitis: 250 or 500 mg twice daily for 5-10* days.
*The safety and effectiveness when administered for <10 days in acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis have not been established.
Uncomplicated Urinary Tract, Skin and Skin-Structure Infections: 250 mg twice daily for 7-10 days.
Uncomplicated Gonorrhea: 1000 mg once with single dose probenecid 1000 mg.
Early Lyme Disease: 500 mg twice daily for 20 days.
Children (Who can Swallow Tablet Whole): Acute Otitis Media and Bacterial Maxillary Sinusitis: 250 mg twice daily for 10 days.
Injection: Adults: Usual Dosage Range: 750 mg to 1.5 g every 8 hrs, usually for 5-10 days.
Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections, Skin-Structure Infections, Disseminated Gonococcal Infections and Uncomplicated Pneumonia: Recommended Dose: 750 mg every 8 hrs.
Severe and Complicated Infections, Bone and Joint Infections: Recommended Dose: 1.5 g every 8 hrs.
Bacterial Meningitis: Recommended Dose: 1.5 g every 6 hrs and should not exceed 3 g every 8 hrs.
Uncomplicated Gonococcal Infection: Recommended Dose: 1.5 g given IM as a single dose together with 1 g of oral probenecid.
Children: Normal Dose: 50-100 mg/kg/day, and may be increased to 150 mg/kg/day in cases of bone and joint infections, and 200-240 mg/kg/day for bacterial meningitis in equally divided doses, every 6-8 hrs.
Overdosage
Overdosage of cephalosporins can cause cerebral irritation leading to convulsions. Serum levels of cefuroxime can be reduced by hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Administration
Should be taken with food: Take w/ meals for optimum absorption.
Contraindications
Cefuroxime axetil is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics.
Warnings
Tablets: Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefuroxime axetil, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
Clostridium difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. Clostridium difficile must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over 2 months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Injection: Cefumax should be used with care in patients with hypersensitivity to penicillin.
In the clinical and laboratory tests, cross-allergenicity between penicillin and cephalosporin was ascertained although there were rare cases of patients who have demonstrated allergic reactions to both of these 2 drugs. Some cases of anaphylactic shock were reported especially following the parenteral administration.
During pregnancy and children <3 months, cefumax should be used in cases of absolute necessity and under direct medical control.
Clostridium difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. Clostridium difficile must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over 2 months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Injection: Cefumax should be used with care in patients with hypersensitivity to penicillin.
In the clinical and laboratory tests, cross-allergenicity between penicillin and cephalosporin was ascertained although there were rare cases of patients who have demonstrated allergic reactions to both of these 2 drugs. Some cases of anaphylactic shock were reported especially following the parenteral administration.
During pregnancy and children <3 months, cefumax should be used in cases of absolute necessity and under direct medical control.
Special Precautions
Tablet: As with other broad-spectrum antibiotics, cefuroxime axetil should be prescribed with caution in individuals with history of colitis. Prolonged administration of cefuroxime axetil may also result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible microorganisms. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Cephalosporins, including cefuroxime axetil, should be given with caution to patients receiving concurrent treatment with potent diuretics are suspected of adversely affecting renal function.
Cephalosporins may be associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Those at risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment of poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a protracted course of antimicrobial therapy, and patients previously stabilized on anticoagulant therapy. Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at risk and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated.
Injection: In case of pronounced renal insufficiency, the dosage of Cefumax has to be reduced according to the renal function test.
The concomitant administration with other nephrotoxic drug (kanamycin, streptomycin, colistin, viomycin, polymixin, neomycin, gentamycin, etc) increases the renal toxicity. Consequently, the renal function has to be observed cautiously.
The long-term administration of Cefumax may cause the development of nonsusceptible bacteria, therefore, appropriate therapeutic measures must be taken in such cases.
The administration of cephalosporins may interfere with the results of some laboratory tests, causing false-positive reaction of the glycosuria according to the methods of Benedict's, Fehling's and Clinitest, but not in accordance with enzyme-based tests. During treatment with cephalosporins, a false-positive result may occur in the direct Coombs' test.
Use in pregnancy: Pregnancy Category B: Reproduction studies have been performed on mice at doses up to 3200 mg/kg/day (14 times the recommended maximum human dose based on mg/m2) and in rats at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (9 times the recommended maximum human dose based on mg/m2) and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cefuroxime axetil. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, Cefumax should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Use in lactation: Because cefuroxime is excreted in human milk, consideration should be given to discontinuing nursing temporarily during treatment with cefuroxime axetil.
Cephalosporins, including cefuroxime axetil, should be given with caution to patients receiving concurrent treatment with potent diuretics are suspected of adversely affecting renal function.
Cephalosporins may be associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Those at risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment of poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a protracted course of antimicrobial therapy, and patients previously stabilized on anticoagulant therapy. Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at risk and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated.
Injection: In case of pronounced renal insufficiency, the dosage of Cefumax has to be reduced according to the renal function test.
The concomitant administration with other nephrotoxic drug (kanamycin, streptomycin, colistin, viomycin, polymixin, neomycin, gentamycin, etc) increases the renal toxicity. Consequently, the renal function has to be observed cautiously.
The long-term administration of Cefumax may cause the development of nonsusceptible bacteria, therefore, appropriate therapeutic measures must be taken in such cases.
The administration of cephalosporins may interfere with the results of some laboratory tests, causing false-positive reaction of the glycosuria according to the methods of Benedict's, Fehling's and Clinitest, but not in accordance with enzyme-based tests. During treatment with cephalosporins, a false-positive result may occur in the direct Coombs' test.
Use in pregnancy: Pregnancy Category B: Reproduction studies have been performed on mice at doses up to 3200 mg/kg/day (14 times the recommended maximum human dose based on mg/m2) and in rats at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (9 times the recommended maximum human dose based on mg/m2) and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cefuroxime axetil. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, Cefumax should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Use in lactation: Because cefuroxime is excreted in human milk, consideration should be given to discontinuing nursing temporarily during treatment with cefuroxime axetil.
Use In Pregnancy & Lactation
Use in pregnancy: Pregnancy Category B: Reproduction studies have been performed on mice at doses up to 3200 mg/kg/day (14 times the recommended maximum human dose based on mg/m2) and in rats at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (9 times the recommended maximum human dose based on mg/m2) and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cefuroxime axetil. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, Cefumax should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Use in lactation: Because cefuroxime is excreted in human milk, consideration should be given to discontinuing nursing temporarily during treatment with cefuroxime axetil.
Use in lactation: Because cefuroxime is excreted in human milk, consideration should be given to discontinuing nursing temporarily during treatment with cefuroxime axetil.
Adverse Reactions
Tablet: The following hypersensitivity reactions with cefuroxime axetil have been reported: Anaphylaxis, angioedema, pruritis, rash, serum sickness-like reaction, urticaria, pseudomembranous colitis (see Warnings), hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia, increased prothrombin time, hepatic impairment, including hepatitis and cholestasis, jaundice, seizure, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, renal dysfunction. The following are also reported: Diarrhea/loose, nausea/vomiting; transient LDH, AST and ALT elevation; eosinophilia, abdominal pain and cramps, flatulence, indigestion, headache, vaginitis, vulvar itch, rash, hives, itch, dysuria, chills, chest pain, shortness of breath, mouth ulcers, swollen tongue, sleepiness, thirst, anorexia, positive Coombs' test, and mild to moderate hearing loss.
Injection: Adverse reactions are mainly gastrointestinal disorders and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. The appearance of the latter is mostly in individuals who have previously shown hypersensitivity reactions to pharmaceutical products and other substances and in those who have a previous case history of allergy, asthma, hay fever and urticaria.
In general, patients treated with cephalosporins have had the following undesirable reactions reported during or after treatment: Glossitis, nausea, vomiting, gastric pyrosis, abdominal pain and diarrhea. Very rare: Cutaneous rash, pruritus, urticaria and arthralgia were also reported.
Occasionally, transient and recoverable changes in some laboratory parameters eg, eosinophilia, leukopenia, and increased serum transaminase, total bilirubin and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were reported. Other reactions observed were vertigo with sensation of thoracic constriction and candida vaginitis, with appearance of the latter related to the development of nonsusceptible organisms. These adverse reactions should be treated properly and closely monitored by physicians to determine whether a discontinuation of therapy is necessary.
Injection: Adverse reactions are mainly gastrointestinal disorders and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. The appearance of the latter is mostly in individuals who have previously shown hypersensitivity reactions to pharmaceutical products and other substances and in those who have a previous case history of allergy, asthma, hay fever and urticaria.
In general, patients treated with cephalosporins have had the following undesirable reactions reported during or after treatment: Glossitis, nausea, vomiting, gastric pyrosis, abdominal pain and diarrhea. Very rare: Cutaneous rash, pruritus, urticaria and arthralgia were also reported.
Occasionally, transient and recoverable changes in some laboratory parameters eg, eosinophilia, leukopenia, and increased serum transaminase, total bilirubin and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were reported. Other reactions observed were vertigo with sensation of thoracic constriction and candida vaginitis, with appearance of the latter related to the development of nonsusceptible organisms. These adverse reactions should be treated properly and closely monitored by physicians to determine whether a discontinuation of therapy is necessary.
Drug Interactions
Tablet: Concomitant administration of probenecid with cefuroxime axetil tablets increases the area under the serum concentration versus time curve by 50%. The peak serum cefuroxime concentration after a 1.5-g single dose is greater when taken with 1 g of probenecid (mean=14.8 mcg/mL) than without probenecid (mean=12.2 mcg/mL).
Drugs that reduce gastric acidity may result in a lower bioavailability of cefuroxime axetil compared with that of fasting state and tend to cancel the effect of postprandial absorption. In common with other antibiotics, cefuroxime axetil may affect the gut flora, leading to lower estrogen reabsorption and reduced efficacy of combined oral estrogen/progesterone contraceptives.
Drugs that reduce gastric acidity may result in a lower bioavailability of cefuroxime axetil compared with that of fasting state and tend to cancel the effect of postprandial absorption. In common with other antibiotics, cefuroxime axetil may affect the gut flora, leading to lower estrogen reabsorption and reduced efficacy of combined oral estrogen/progesterone contraceptives.
Storage
Store at temperature not exceeding 30°C. Protect from light.
Action
Pharmacology: Injection: Cefumax powder for injection is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, containing cefuroxime sodium as the active ingredient. Cefuroxime is a semisynthetic cephalosporin.
Microbiology: The bactericidal action of cefuroxime results from the inhibition of the bacterial cell wall synthesis. To achieve this, the integrity of β-lactam group is essential. The presence of a methoxyimine group prevents cefuroxime from breakdown by endo-β-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria (Enterobacter spp and indole-positive Proteus). So, cefuroxime is active against other cephalosporin-resistant strains. Treatment of infections caused by strains susceptible to cefuroxime: Respiratory Tract Infections: Bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, lung abscess, empyema and bronchiectasis.
Ear, Nose and Throat Infections: Tonsillitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, mastoiditis.
Genitourinary Tract Infections: Pyelitis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis , epididymitis, gonococcal urethritis, metritis, parametritis and adnexitis.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Ecpyesis, cellulitis, phlegmon gangrene, mastitis and wound infections.
Pharmacokinetics: Tablet: After oral administration, cefuroxime axetil is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and rapidly hydrolyzed by nonspecific esterases in the intestinal mucosa and blood to cefuroxime; absorption is enhanced in the presence of food. Cefuroxime is subsequently distributed throughout the body including pleural fluid, sputum bone, synovial fluid, and aqueous humour, but only achieves therapeutic concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) when the meninges are inflamed. Cefuroxime crosses the placenta and has been detected in breast milk. Approximately 50% of serum cefuroxime is bound to protein. Serum pharmacokinetic parameters are as follows: (See Table.)
Microbiology: The bactericidal action of cefuroxime results from the inhibition of the bacterial cell wall synthesis. To achieve this, the integrity of β-lactam group is essential. The presence of a methoxyimine group prevents cefuroxime from breakdown by endo-β-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria (Enterobacter spp and indole-positive Proteus). So, cefuroxime is active against other cephalosporin-resistant strains. Treatment of infections caused by strains susceptible to cefuroxime: Respiratory Tract Infections: Bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, lung abscess, empyema and bronchiectasis.
Ear, Nose and Throat Infections: Tonsillitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, mastoiditis.
Genitourinary Tract Infections: Pyelitis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis , epididymitis, gonococcal urethritis, metritis, parametritis and adnexitis.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Ecpyesis, cellulitis, phlegmon gangrene, mastitis and wound infections.
Pharmacokinetics: Tablet: After oral administration, cefuroxime axetil is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and rapidly hydrolyzed by nonspecific esterases in the intestinal mucosa and blood to cefuroxime; absorption is enhanced in the presence of food. Cefuroxime is subsequently distributed throughout the body including pleural fluid, sputum bone, synovial fluid, and aqueous humour, but only achieves therapeutic concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) when the meninges are inflamed. Cefuroxime crosses the placenta and has been detected in breast milk. Approximately 50% of serum cefuroxime is bound to protein. Serum pharmacokinetic parameters are as follows: (See Table.)
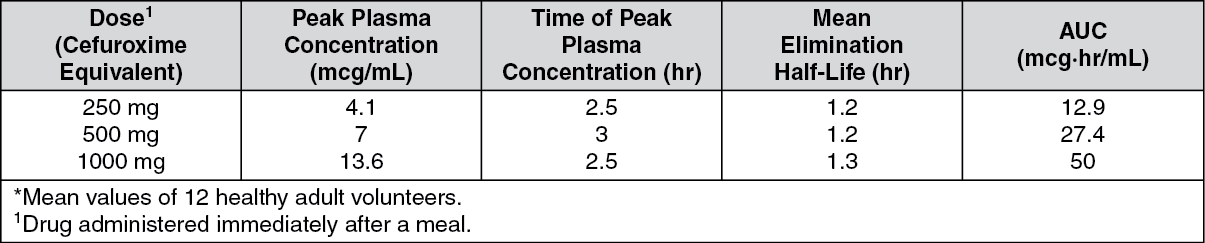
Cefuroxime is excreted unchanged by glomerular filtration and renal tubular secretion, and high concentrations are achieved in the urine. Small amounts are excreted in bile. Dialysis reduces plasma concentrations.
The axetil moiety is metabolized to acetaldehyde and acetic acid.
The axetil moiety is metabolized to acetaldehyde and acetic acid.
MedsGo Class
Cephalosporins
Features
Dosage
500 mg
Ingredients
- Cefuroxime
Packaging
Film-Coated Tablet 100's
Generic Name
Cefuroxime Axetil
Registration Number
DR-3442-01
Classification
Prescription Drug (RX)
Reviews
No reviews found
Product Questions
Questions

